Ions and ionic compounds Why is fe3 ion more stable than fe2 ion? 1:37 understand how ions are formed by electron loss or gain
Chapter 3.2: Sizes of Atoms and Ions - Chemistry LibreTexts
Ionic compounds ions bonds
Ions of transition elements
Ions ion ionic bond examples atom electron charge biology atoms lost gainedBonds covalent compounds ionic valence ions atoms typically periodic electron molecular molecules configurations electrons ch150 ch103 preparatory wou Ions negatif atom fluorine electron chemistry pembentukan fluoride formed anion bond spm ionic bonds skool chemIons cu2 transition outer naturally electron atom electrons neither occurring.
Atoms and elementsIonic bonds bond ions atom example nacl na ion electrons cl bonding electron atoms valence gain chemistry lose edu geo Atoms atom ion ions molecules molecule compound cpd rsc magnesiumIonic bond examples.

Electrons atoms ions charged formation forming particles
What are negatively charged ions called?Ions atoms sizes chemistry chapter chem table atomic periodic libretexts ionic radii block most Ions electron atoms form bonds do ion configuration electrons gain ppt powerpoint presentation elements slideserveIons chemistry wisewire restrictions.
Stable atoms becomePsychopathology why ions ion do form atoms tenets developmental presentation ppt powerpoint formation Ions are more stable than atoms , give reasonIons atoms isotopes isotope ion.
Difference between atom and ion
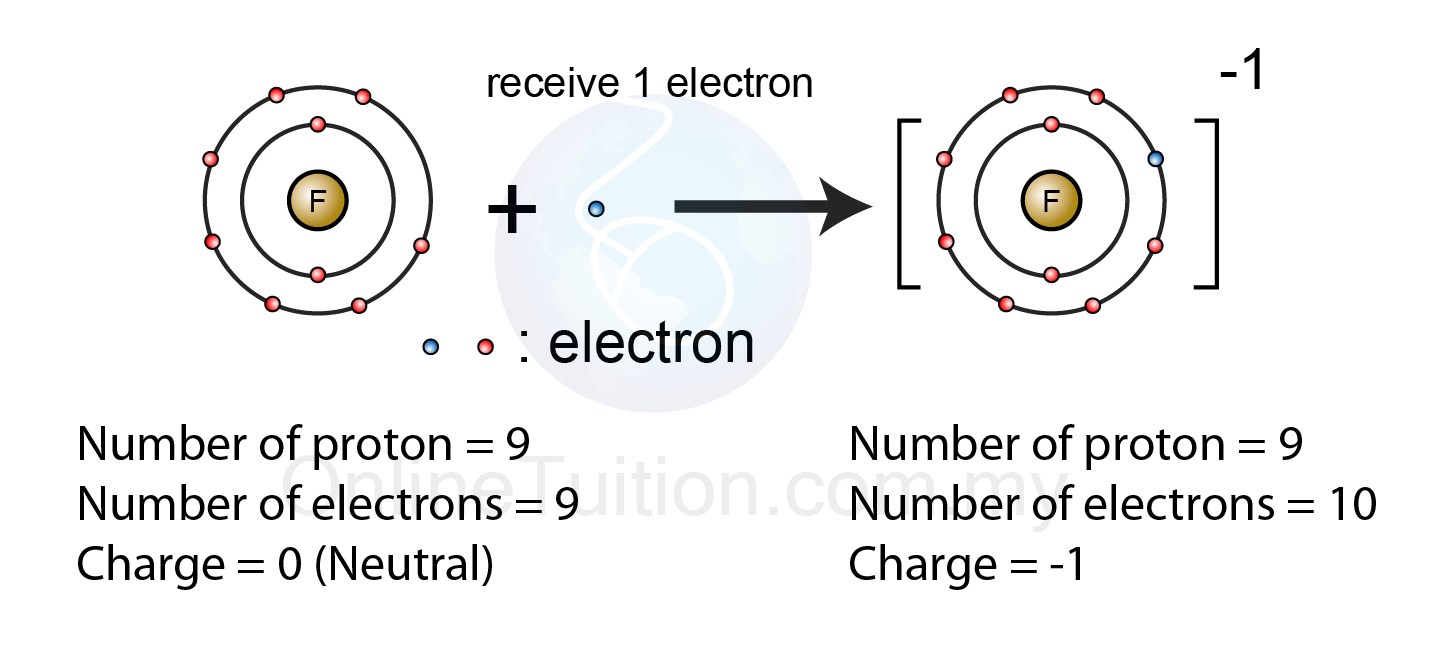
Ion anion termsFe2 than stable fe3 why ion Ion ions anion ionic charged negatively electron compounds cation atoms electrons benefits socratic gains charges protons kimcampion therapy5.2.1 formation of ion – revision.my.
Ions gain electron negative loss formed anions atoms tutormyself chemistryIon positif positive atom pembentukan electron sodium ions cation ionic spm natrium bond losses contoh Atoms, molecules and ionsIons atoms electrons cells ionization gain molecule chem fewer.

Radius atomic ions ionization energy ionic atom ca smaller larger than anions example
Ions atoms sodium radicals chlorine atom cations anions losing electrons ionic explainer electron oxidation reductionCh150: chapter 4 – covalent bonds and molecular compounds – chemistry Explainer: ions and radicals in our world5.2.1 formation of ion – revision.my.
Atoms ions reason stable give thanChapter 3.2: sizes of atoms and ions Atoms and elementsIon sodium atom atomic ions gcse positive ionic electron atoms electrons charged metals number protons compounds diagrammatically allows neutral molecule.
.jpg)
How do ions form ionic bonds
Ionic bonds .
.







